Early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality and carries a substantial risk of recurrence, even after complete resection or adjuvant therapy.

Interim results from the NADIM ADJUVANT trial suggest that adjuvant chemo-immunotherapy may reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with completely resected stage IB–IIIA NSCLC while maintaining an acceptable safety profile.
Building on perioperative evidence from the earlier NADIM and NADIM II studies, this study—led by the Spanish Lung Cancer Group—is the first randomized phase III trial to examine chemo-immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting.
“Several trials have explored the role of adjuvant immunotherapy with variable results, but none of them have examined the combination of chemotherapy plus immunotherapy,” said Mariano Provencio, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda, Madrid, Spain.
Dr. Provencio presented the first interim analysis from the NADIM ADJUVANT trial at the 2025 World Conference on Lung Cancer (WCLC) during the second Presidential Symposium on Monday, September 8.
Trial Design and Background
The open-label, multicenter trial enrolled 206 patients from 30 hospitals across Spain between January 2021 and December 2022. The study criteria included patients with completely resected stage IB (tumors ≥ 4 cm) to IIIA NSCLC, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status of 0 to 1, and no prior systemic therapy.
Eligible patients were randomized 1:1 to either the control group—adjuvant chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles, followed by observation—or the experimental group—chemotherapy plus nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks for four cycles, followed by maintenance nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks for six cycles.
The primary endpoint was disease-free survival (DFS). Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS) and safety. Minimal residual disease (MRD) by Guardant Reveal was assessed using circulating tumor DNA as an exploratory endpoint.
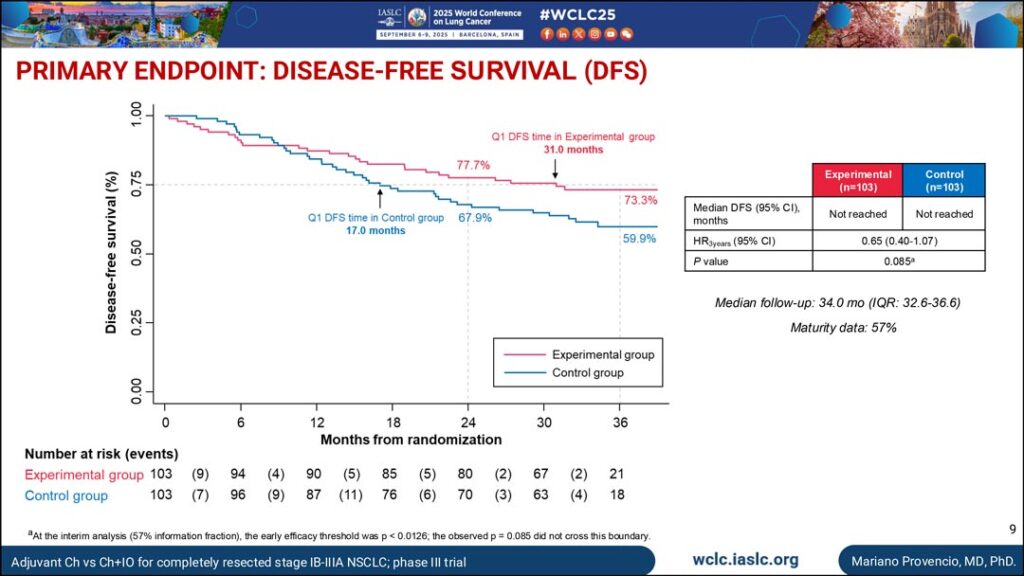
Key Results
After a median follow-up of 34 months, the median DFS was not reached in either group.
However, the first-quartile DFS time was longer in patients in the experimental group (31 months vs. 17 months).
Postoperative MRD was detected in 9.8% of patients in the experimental arm and in 10% of patients in the control arm and was associated with significantly worse DFS (hazard ratio [HR]: 5.7; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.0–31.2; p = 0.045) among patients in the experimental group.
There were 61 occurrences of relapse, recurrence, or death, with 20.4% occurring in the experimental group and 38.8% in the control group. The 3-year relapse rate was lower in patients in the experimental group (26.7% vs. 40.1%).
Dr. Provencio said the 90-day after-surgery landmark analysis supported the benefit of the experimental group (HR = 0.60; 95% CI: 0.37-0.99; p = 0.048). A sensitivity analysis of cancer-specific DFS yielded an HR of 0.54 (95% CI: 0.32–0.93; p = 0.025), favoring the experimental arm.
Treatment compliance was high in both groups (89.3% in the experimental group vs. 90.3% in the control group), and 67% of patients completed nivolumab maintenance therapy.
Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were more frequent in the experimental group (26.2%) compared to the control group (14.5%) during the adjuvant phase and occurred in 10.6% of patients during the nivolumab maintenance phase. Two treatment-related deaths were reported in the experimental arm: one due to pneumonitis and one due to colitis.
Conclusions and Future Directions
Although DFS did not reach statistical significance, Dr. Provencio said the interim results from the NADIM ADJUVANT trial suggest that adjuvant chemo-immunotherapy reduces the risk of recurrence in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA NSCLC, and the regimen has an acceptable safety profile. Additionally, the landmark and sensitivity analyses provided real-world evidence on the DFS endpoint and supported the clinical benefit.
“We included all the patients after surgery, and, as you can see, the postoperative mortality and/or toxicity during the adjuvant period can affect DFS,” Dr. Provencio said. “The sensitivity analysis of cancer-specific DFS was positive, with a HR of 0.54 and a p-value of 0.25.”
The safety profile was consistent with the data from chemo-immunotherapy combinations in other clinical settings. Further, he said the MRD assessment helped identify a subgroup of patients with a poorer prognosis; however, continued follow-up is ongoing and necessary to confirm the long-term effectiveness of this approach.
“The interim results of NADIM ADJUVANT suggest that adding nivolumab to adjuvant chemotherapy can reduce the risk of recurrence and may offer meaningful clinical benefits for patients with completely resected stage IB–IIIA NSCLC,” Dr. Provencio said. “Further follow-up will be essential to confirm long-term efficacy.”
Indeed, in her review of the data, discussant Tina Cascone, MD, PhD, urged caution in interpreting the results as the efficacy boundary was not crossed, so more mature, long-term analysis is needed.
She pointed to higher rates of cardiac and coronary artery disease-related comorbidities in the experimental arm as another reason for careful consideration of the results as these events may have affected the efficacy and safety data. Half the patients who died before the data cutoff had adverse events that were cardiac in nature, she said.
Still, Dr. Cascone said the results are encouraging and the strategy may be relevant for patients undergoing upfront surgery, which is still common outside of neoadjuvant IO pathways. In the future, biomarker-driven personalization will be needed to guide adjuvant strategies, she said.










