The CheckMate 816 trial, which evaluated neoadjuvant nivolumab in combination with chemotherapy, demonstrated a significant survival advantage versus chemotherapy alone in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Additionally, data confirmed a durable event-free survival (EFS) benefit.
Patrick M. Forde, MD, PhD, Trinity St. James’s Cancer Institute, Trinity College Dublin, presented the latest and final overall survival (OS) data of CheckMate 816 during the 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting.
“CheckMate 816 is the only phase III trial of neoadjuvant-only chemoimmunotherapy to demonstrate a statistically significant OS benefit across any resectable solid tumor type,” Dr. Forde said. “This affirms a paradigm shift in the treatment of resectable lung cancer without actionable genomic alterations.”
Study Design
The CheckMate 816 study was designed to examine the potential benefits of adding neoadjuvant nivolumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with resectable NSCLC. Key eligibility criteria included:
- Newly diagnosed stage IB (at least 4 cm) to stage IIIA NSCLC
- Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) 0-1
- No known sensitizing EGFR mutations or ALK fusions
Stratification variables included disease stage, PD-L1 status, and sex. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either three cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone or neoadjuvant chemotherapy and nivolumab.
Surgery was scheduled within 6 weeks of the final cycle of systemic therapy. Post-operative immunotherapy was not mandated; however, optional chemotherapy or radiation was permitted.
The primary endpoints were pathologic complete response (pCR) and EFS. Secondary endpoints included OS, time to death or distant metastases (TTDM), and major pathologic response (MPR).
Key Findings
The final 5-year analysis demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful OS benefit for the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm. The 5-year OS rate was 65% for the combination, compared with 55% for chemotherapy alone. Additionally, there were improvements in lung cancer-specific survival (75% vs. 65%).
The OS benefit was consistent across various disease stages and PD-L1 expression levels.
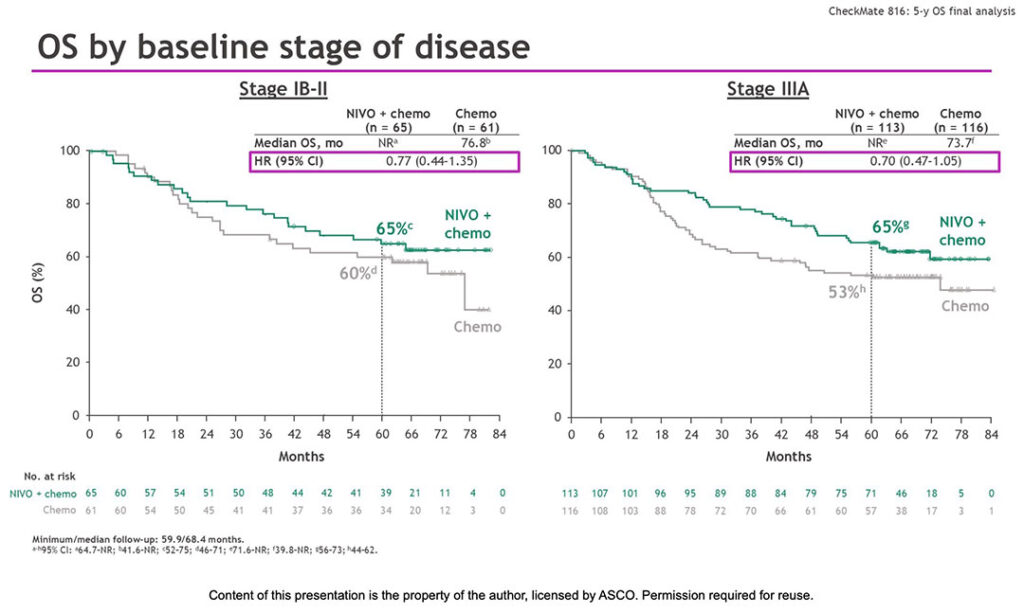
“A comparable OS benefit was seen for both stage IB-II disease (65% vs. 60%) and stage IIIA disease (65% vs. 53%), with hazard ratios of 0.77 and 0.7, respectively,” Dr. Forde said. “Benefit was seen across PD-L1 strata, with enhanced benefit for PD-L1-positive tumors.”
pCR and Survival Analysis
Patients who achieved a pCR status experienced a significant reduction in the risk of death. At 5 years, 95% of patients with a pCR in the nivolumab-chemotherapy group were still alive, compared with 56% of those without pCR status.
“Among those with pCR after nivolumab plus chemotherapy, there was a 90% reduction in the risk of death by 5 years versus those without,” Dr. Forde said.
He noted that the safety profile of neoadjuvant nivolumab combined with chemotherapy was consistent with previous reports.
ctDNA Clearance
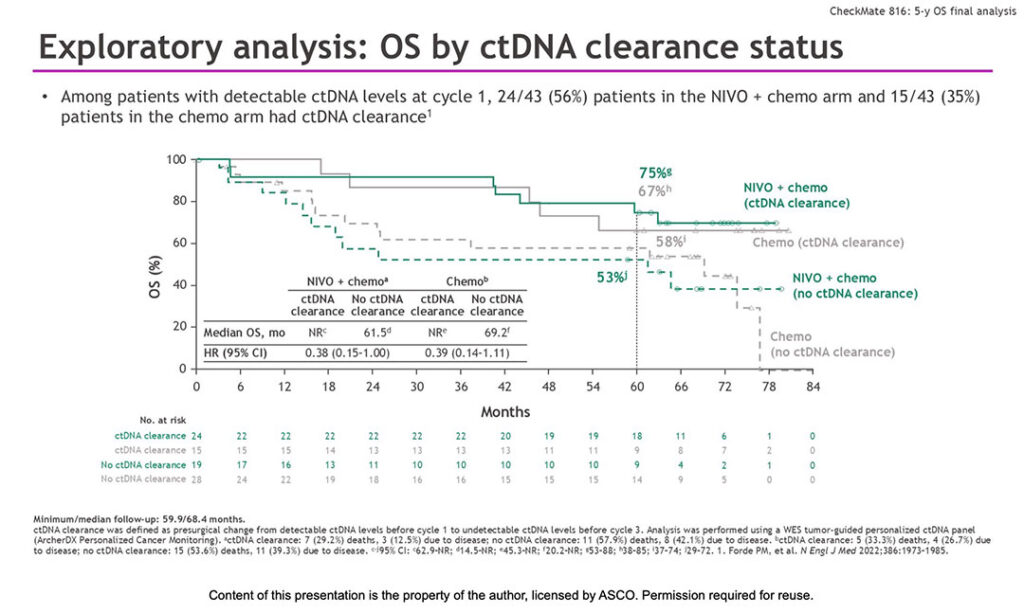
CheckMate 816 also showed that presurgical clearance of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) was associated with long-term OS benefits, regardless of treatment. ctDNA clearance was more common in patients treated with nivolumab in combination with chemotherapy.
Among patients with detectable ctDNA at cycle one, 56% in the nivolumab-chemotherapy group, compared to 35% in the chemotherapy-alone group, achieved ctDNA clearance by cycle three during the neoadjuvant period.
“Seventy-five percent of patients who cleared ctDNA with nivolumab plus chemotherapy were alive at 5 years versus 53% who did not clear ctDNA,” Dr. Forde said. “A similar OS benefit was seen with clearance of ctDNA with chemotherapy.”
Clinical Impact
Dr. Forde said CheckMate 816’s final OS results reinforce neoadjuvant chemo-immunotherapy with nivolumab and chemotherapy as a new standard-of-care treatment for resectable NSCLC. The data provide compelling evidence that this combination treatment improves the likelihood of long-term survival outcomes, particularly for patients achieving pCR and ctDNA clearance.










